J-QAM
User Manual For V2
Installation:
To install the program run the downloaded program jqamv2_setup.exe. The install wizard will guide you through the rest of the installation.
Running the program:
You will find a program shortcut in your start menu. Click Start , J-QAM , J-QAM V2. If this is the first time you have run the program a window will display telling you fftw is finding a fast implementation of an fft. Once this is gone the program is loaded.
Configuring
the program:
Upon running the program, a default window will be showing.
If all you want to do is use it as a demodulator, chances are selecting file-start is enough.
Else, click the options-settings from the menu bar. The following window should be showing.
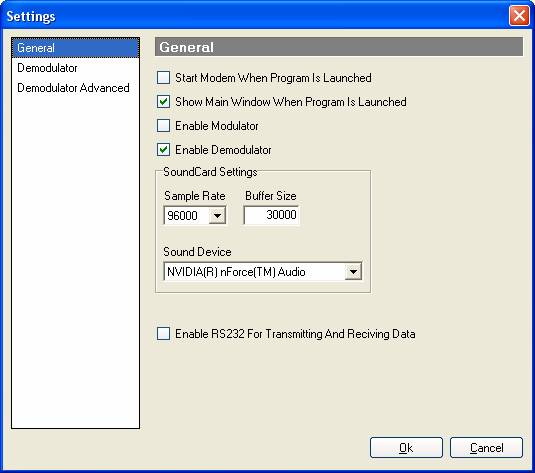
First, configure “SoundCard Settings”. Choose the “sample rate” for your sound card, I recommend 96000 but if your computer does not work well with this setting try something lower like 48000. The “buffer size” controls the size of the audio buffer and the value of 30000 should be adequate. Choose your “Soundcard Device” from the list.
Next,
Decide which checkboxes you want
to activate.
- Enable
Modulator
Select this if you want the program to be used as a modulator (makes the sound)
- Enable
Demodulation
Select this if you want the program to be used as a demodulator (decodes the sound)
- Show
Main Window when Program Is launched
- Start
when program is run
This option will start the modem modulating and/or demodulating the the program is launched.
- Enable
RS232 for transmitting and receiving data.
If this option is checked then the designated serial port can be used to send and receive data from the program.
You will then have to select your serial port and speed.
Configuring the demodulator.
From the settings window click on “Demodulator”
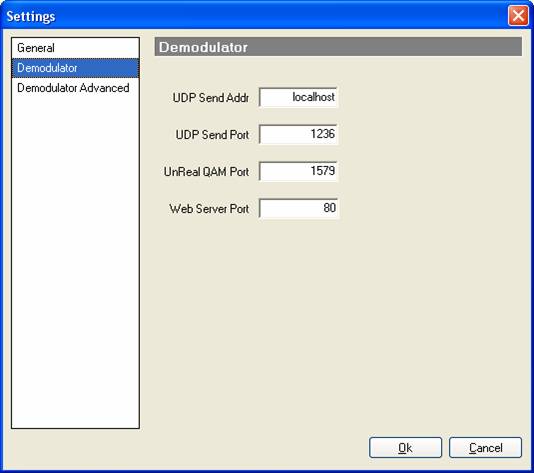
Demodulator
Settings (General).
- UDP
Send Addr
If you intend to receive UDP packets the set this to where you want them to be sent. “localhost”, “127.0.0.1”, “192.168.0.1” are common for the local computer.
- UDP Send Port
If you intend to receive UDP packets the set this to what port you want them to use.
- Unreal QAM Port
If you intend to receive Unreal media this port is the address you connect “streaming media player” to. You will have to download “streaming media player” for this go to http://www.umediaserver.net/umediaserver/download.html.
- Web Server Port
What port the web server will run on. 80 is the standard.
“Demodulator Advanced” is the window where all the settings of the acquisition of the signal and tracking of it live. Experiment with these if you are feeling keen.
Click
“OK”, select File-start, and the
program will hunt for a signal.
Configuring the modulator.
From
the settings window click on
“Modulator”
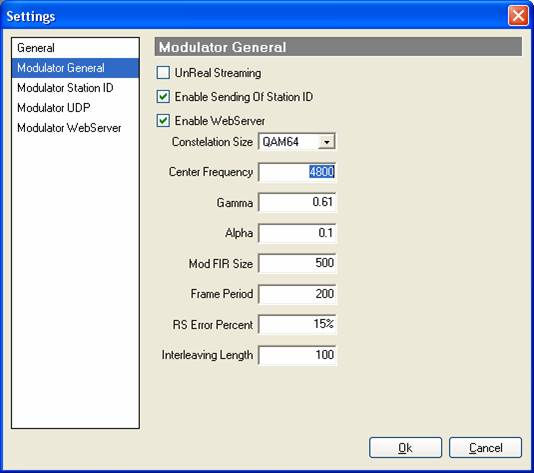
Next,
configure “QAM settings”. Decide
which checkboxes you want to activate.
- Unreal
Streaming
Select this if you want the program to send audio and video
- Enable
Sending Of Station ID
Sends the name of your station at regular intervals.
- Enable
WebServer
If this option is selected the program sends files to the in computers that are demodulating the signal. It uses only unutilized bandwidth and is therefore perfect when sending unreal media to describe what your station is about.
- Constellations
size
Chooses what constellation size you want. Either 16 or 64. 64 will allow 67% more throughput given the same bandwidth as 16. The catch is that 64 is more likely to not lock and will receive more errors than 16.
- Center
frequency
The carrier frequency is this frequency. Choose this value so it is in the middle of your available bandwidth. Values from 1200 to 12000 should be OK on normal sound cards.
- Gamma
Gamma is a setting that controls the number of symbols sent for each oscillation of the frequency. A value of 0.75 means that one symbol is sent every 75% of an oscillation cycle. This means that smaller values allow you to get a higher throughput, but the program finds it harder to determine what symbol was sent when gamma is small, also the smaller gamma is the smaller alpha must be. For example, if you want gamma to be equal to 0.54, alpha must be no bigger than about 0.1. You should choose a value between 0.54 and 1. I suggest you use a program like “spectrum lab” to see what difference alpha and gamma have on the audio output spectrum, you can also use the spectrum display when demodulating in this program to see visually how alpha and gamma affect the output wave.
- Alpha
Alpha is a setting that tells the program what sort of filters to use. Small values produce a signal output that uses less bandwidth, but the “FIR size” of the modulator and at the demodulator must be bigger. You should choose a value between 0.1 and 1.
- Mod
FIR Size
this setting controls the size of the modulation filter. The higher the number the nicer the output wave looks. The value of 200 to 900 should be fine.
- Frame
period
every so often the program must send a frame to allow the receiver in the information to know the transmitters settings. This is a frame, which is 10 bytes long. A value of a few hundred should be fine. The bigger its value is the longer a receiver has to wait but that is all.
- RS
Error percent
On top of TCM the program uses Reed Solomon forward error correction. This setting controls how much it should use. The higher this number is the more bandwidth is used for error correction. If you wish to set this at 50% half of your bandwidth is used for error correction. A value of 10% to 20% should be okay but experiment to see.
- Interleaving
length
this is used by the Reed Solomon code in combating burst errors. The bigger this value is the more the program is immune to burst errors. The catch is the latency goes up. Experiment with this.
Your data rate in bits per second can be worked out using the following formula.
For QAM16 datarate= ((100- RSErrorPercent)/100)*3*CenterFrequency/Gamma
For QAM64 datarate= ((100- RSErrorPercent)/100)*5*CenterFrequency/Gamma
Your bandwidth in Hertz will be
Bandwidth=(1+alpha)*CenterFrequency/Gamma
And remember
2*gamma-1 should be greater than alpha.
Station ID
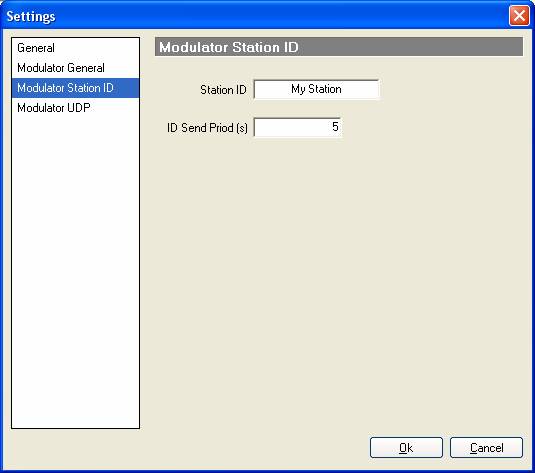
- Station
ID
you can call your stations whenever you want and get J-QAM to broadcast it to all receivers so they know who you are.
- ID
send period
controls how often you want to send your station ID in seconds.
Modulator UDP
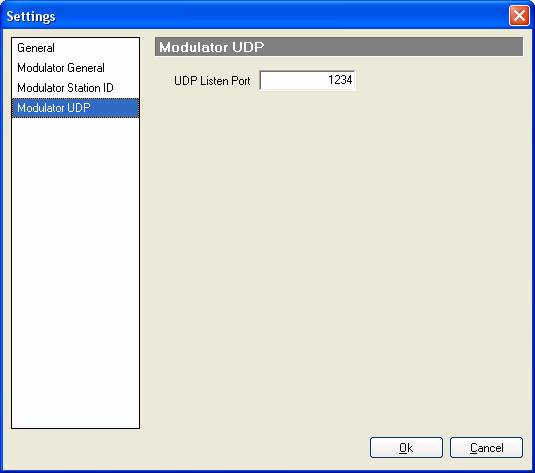
- UDP
listen port.
This is the port that J-QAM will listen for UDP packets.
Modulator Unreal Media
To run unreal media you will need to download “unreal media server”, “unreal media live server” go to http://www.umediaserver.net/umediaserver/download.html to get the two programs needed.
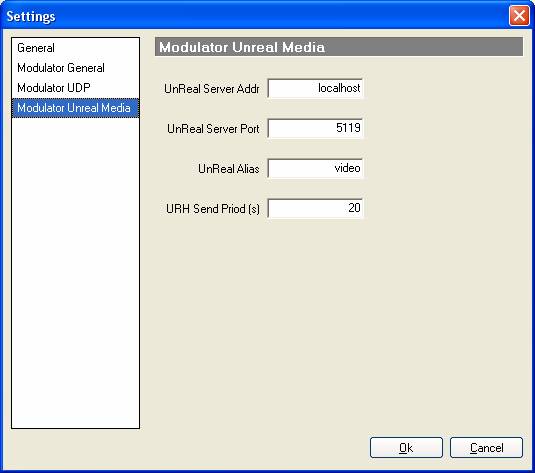
- Unreal
server address.
this is the Internet’s address on which the unreal media server is run on
- Unreal
server port
this is the port on which unreal media server is running. 5119 is unreal media server’s default, and normally this value should be fine.
- Unreal
alias
this is the alias by which J-QAM will try to connect to the unreal media server.
- URH
send period
every so often J-QAM must send an unreal header to all receiving J-QAMs in order to inform them what unreal media is being sent. Any value should be okay but the bigger the value is the longer the receiver must have to wait.
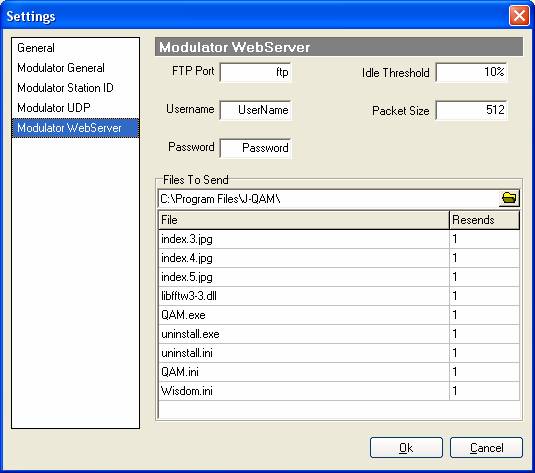
Modulator web server.
These are the files that J-QAM sends when there is sufficient bandwidth. Enter the size of the packet’s you wish to send, 512 should be adequate. The program only sends files when the program is not sending anything else, to do this you must specify the idle threshold. A small idle threshold means the program waits for very little activity before sending a packet of a file. Setting this value to 5% or 10% should be fine. To allow you to change files while the program is still sending files I have added an FTP server to my program. To have access to this FTP server you have to enter a port you want (normally “ftp” is used), what username, and what password you want. Click on the little yellow folder and browse for the file directory that you wish to be sent, all files in this directory can be sent but no directories of this directory. Because files are sent continuously in rotation, “Resends” allow you to specify on average how many times you send a particular file for each rotation. Zero means the file will never be sent and larger values will be sent more regularly.
Received files are stored in a folder named after the station ID where QAM.exe resides. The program allows easy access to these stored files by running a Web server which runs on the port “web server port”. To access it, selecting view-webserver from the main window will launch Firefox or Outlook express and open it. The web server interface looks like the picture below.
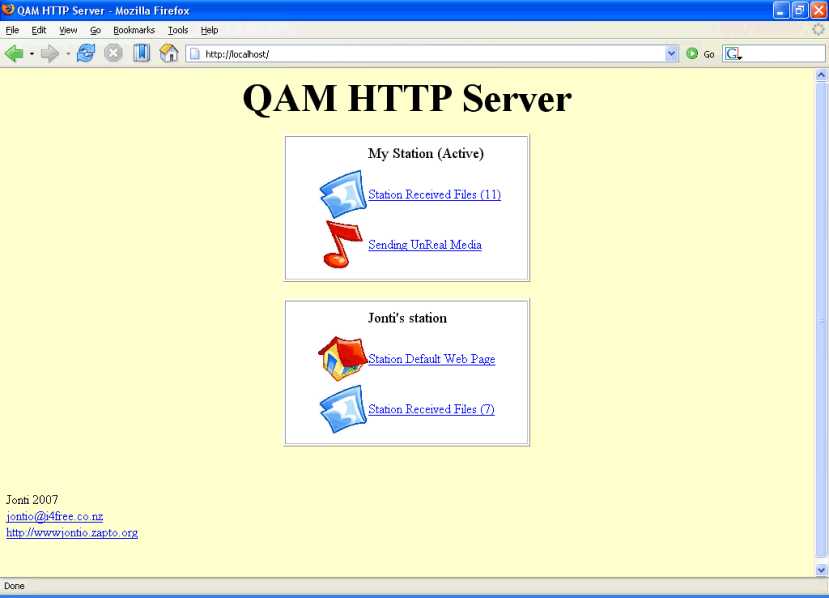
In the settings window OK excepts your settings whilst cancel reverts back to the previous setting.
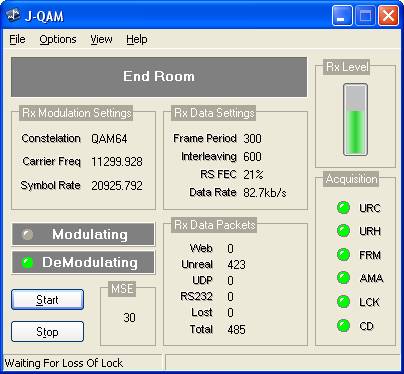
What
all the things mean.
- Rx
Level
shows the amplitude of the received signal
- URH
lights up when the program receives and unreal header packet.
- FRM
lights up when the program receives a frame.
- AMA
lights up when the program uses many moduli for equalization.
- OverF
lights up when data is wishing to be sent faster than the program can actually send it. If you get this lighting up you have to do something about it.
- URC
lights up when an UnReal media player connects to my program.
- URS
lights up when my program connects to an unreal media server.
- Modulating
lights up when the program is modulating (making sound)
- DeModulating
lights up when the program is demodulating (decoding sound)
- CD
lights up when the program has got a possible setting to try.
- LCK
lights up when the program has locked on to the symbol and carrier frequencies and phases.
- MSE
mean square error. Gives a value for the quality of the received signal. The smaller the value the better. (this is a very important parameter for the program and is used in many places. It’s even used to determine which is the right way up for the constellation)
- Buffer
level
shows how much of the transmitter but there is used. When it gets to the top you will get an overflow.
- Data
rate
shows the effective data rate you have got after the over heads have been accounted for.
Items from the “view” menu.
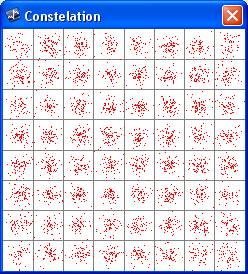
Constellation:
The constellation window gives a visual output of the received symbols.
Console:
The console window gives a display of any RS232 data or text packets. It also allows you to send text packets. Its main use is for testing purposes. Enter characters you want to send in the bottom and characters received will appear in the top.
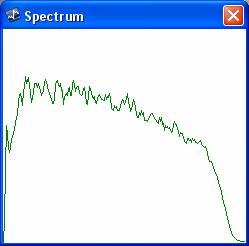
spectrum:
The spectrum window shows what frequencies are being used. If you’re listening to a valid signal you should get something that resembles the following picture.
frequencies:
the frequencies window shows you what frequency settings are probable.
reception:
the reception window shows you the current status of demodulation.
transmission:
the transmission window shows you the current status of modulation.
Web page:
Will open your web browser and loaded J-QAM’s web server address
Starting the modulator/demodulator:
To start the modulator/demodulator simply click the start button in the main window. To stop the modulator/demodulator simply click the stop button in the main window. These are also available from File-start, and File-stop.
Jonti Olds
Email jontio@i4free.co.nz
Home Page https://jontio.zapto.org
Product
Page https://jontio.zapto.org/hda1/paradise/QAM.htm
23/3/2008